To date, the Pressure-Enabled Drug Delivery™ (PEDD™) approach that powers the TriNav Infusion System has been used in over 17,000 procedures. Why are many interventional radiologists selecting the TriNav Infusion System to deliver TARE and TACE as liver cancer treatment for their patients?
Perhaps it is because there is a growing body of clinical evidence showing that the PEDD approach can result in increased targeted therapy penetration, decreased nontarget delivery and enhanced tumor response.1-5 It has been shown to help overcome intratumoral pressure (ITP) more effectively than traditional microcatheters,1,6-8 and it may enable liver tumor downstaging and bridging to transplant.1,9
Time for a demo?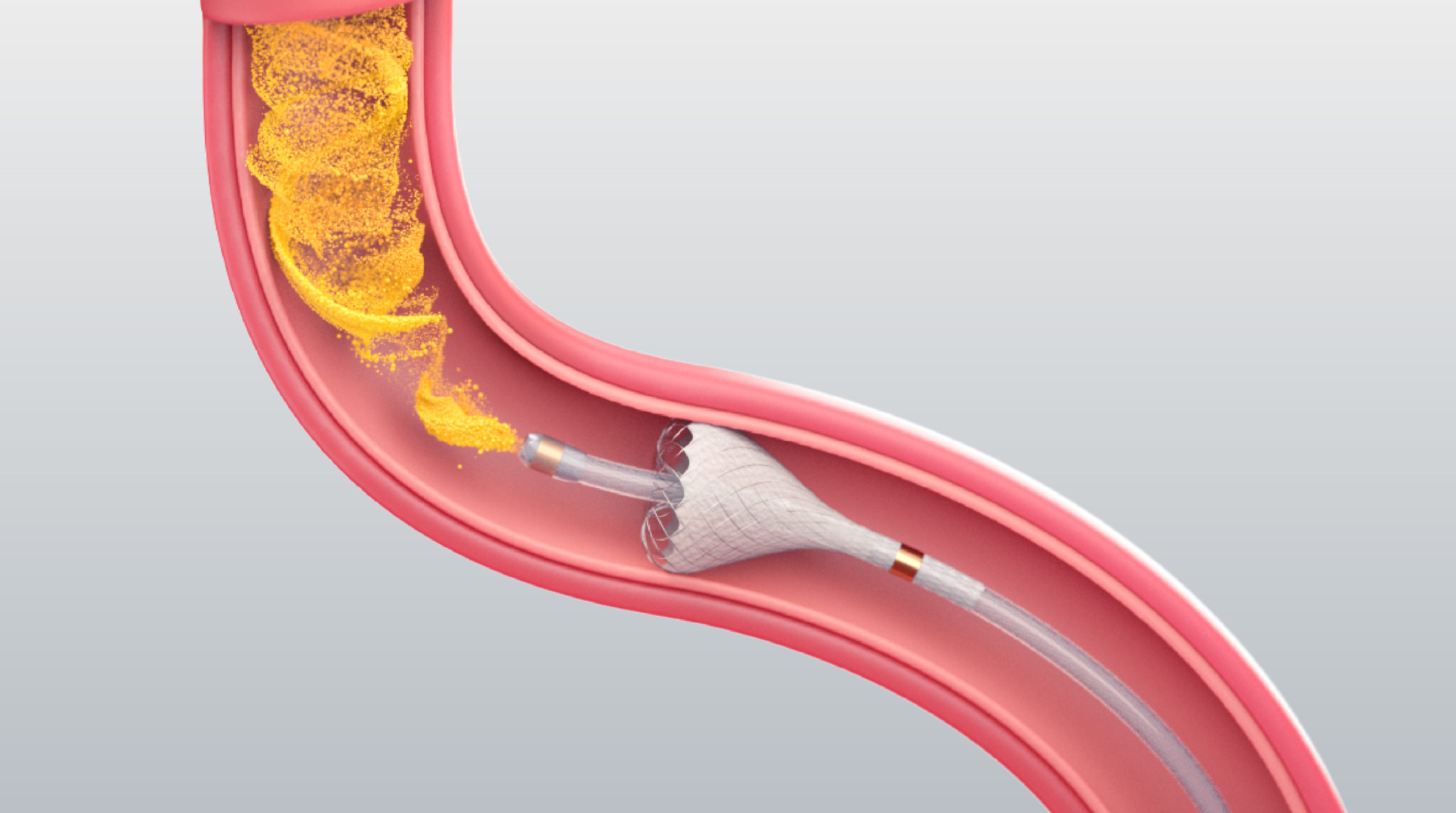
So now may be the time to ask yourself, “Am I delivering all I can for my patients?”
With a demo, your TriSalus representative can help you see how the TriNav Infusion System may benefit your patients and your practice.
Fits seamlessly into current liver cancer treatments and workflows
The TriNav Infusion System works with the therapy options you are using today, including TACE and TARE. Your TriSalus representative can discuss how the simple-to-use TriNav Infusion System can be integrated seamlessly into your current workflow — utilizing preparation steps and processes similar to what you already use.
See the PEDD approach in action
It is the PEDD approach and the functionality of the TriNav Infusion System with SmartValve® technology that may make the difference in therapy delivery. The PEDD approach with SmartValve technology can increase intravascular pressure beyond what the cardiovascular system can generate on its own,10 which may help open collapsed vessels in the tumor and enable deeper perfusion.1,6
Seeing it in action is better than words alone. Your TriSalus representative can share a video that will show you how the PEDD approach that powers the TriNav Infusion System works inside a simulated vessel, compared to traditional microcatheters, and can talk you through every detail.
Clinical evidence relevant to your own cases — possibly even your next one
Your practice, your patients and your needs are unique. Your TriSalus representative can compile and present information that is relevant to your own cases, including case studies, radiographic evidence and supporting data. In fact, they can help you see why using the TriNav Infusion System might be beneficial as you tackle your next liver cancer case.
Why not schedule a demo today?
A strong and growing body of clinical evidence supports the benefits of the PEDD approach that powers the TriNav Infusion System.1-5
Rx Only. For the safe and proper use of the TriNav device, refer to the Instructions for Use.
Indications for Use: The TriNav Infusion System is intended for use in angiographic procedures. It delivers radiopaque media and therapeutic agents to selected sites in the peripheral vascular system.11
Contraindications: TriNav is not intended for use in the vasculature of the central nervous system (including the neurovasculature) or central circulatory system (including the coronary vasculature).11
REFERENCES:
1. Titano JJ, Fischman AM, Cherian A, et al. End-hole versus microvalve infusion catheters in patients undergoing drug-eluting microspheres-TACE for solitary hepatocellular carcinoma tumors: a retrospective analysis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2019;42(4):560-568.
2. Pasciak AS, McElmurray JH, Bourgeois AC, Heidel RE, Bradley YC. The impact of an antireflux catheter on target volume particulate distribution in liver-directed embolotherapy: a pilot study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015;26(5):660-669.
3. Katz SC, Guha P, Hardaway JC, et al. HITM-SURE: Phase Ib CAR-T hepatic artery infusion trial for stage IV adenocarcinoma using Pressure-Enabled Drug Delivery technology. Abstract presented at: Annual Meeting of Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer; November 7-11, 2018; Washington, D.C. Abstract P318.
4. d’Abadie P, Walrand S, Goffette P, et al. Antireflux catheter improves tumor targeting in liver radioembolization with resin microspheres. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2021;27:768–773.
5. Katz SC, Moody AE, Guha P, et al. HITM-SURE: Hepatic immunotherapy for metastases phase Ib anti-CEA CAR-T study utilizing pressure enabled drug delivery. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8(2):e001097.
6. Data on file (REP-0362). TriSalus Life Sciences, 2021.
7. Guan YS, He Q, Wang MQ. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization: history for more than 30 years. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2012;2012:480650.
8. Villanueva A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(15):1450-1462.
9. Kim AY, Frantz S, Krishnan P, et al. Short-term imaging response after drug-eluting embolic trans-arterial chemoembolization delivered with the Surefire Infusion System for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoSOne. 12(9):e0183861.
10. Data on file (CEA 001 trial). TriSalus Life Sciences, 2019.
11. TriSalus TriNav Infusion System, Instructions for Use.